Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems and Their Components
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems: An Overview and Component Analysis
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are complex technological assemblies designed to control and maintain optimal indoor environmental quality (IEQ). Their primary function is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality (IAQ) by regulating temperature, humidity, and air purity within enclosed spaces. HVAC is a critical component of modern building infrastructure, essential for health, productivity, and energy efficiency.
I. Core Functions of HVAC
HVAC systems integrate three fundamental processes to condition air:
1. Heating
The process of adding thermal energy to an indoor space to raise the temperature to a set point, typically achieved through combustion (furnaces) or heat transfer (heat pumps).
2. Cooling (Air Conditioning)
The process of removing heat and controlling relative humidity. This is accomplished via a refrigeration cycle that transfers thermal energy from the interior to the exterior environment.
3. Ventilation
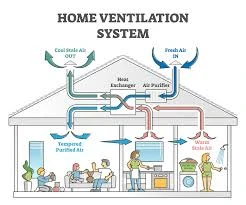
The intentional introduction of fresh outdoor air into a building, and the simultaneous removal of stale indoor air. Ventilation is vital for diluting contaminants, controlling odors, and managing carbon dioxide levels.
II. Key Components of HVAC Systems
An HVAC system is comprised of several interconnected devices working in tandem to deliver conditioned air:
A. Air Processing Units
Air Handling Unit (AHU): A large, centralized piece of equipment that typically contains the fan, heating/cooling coils, filters, and sound attenuators. It conditions and circulates air through the building's ductwork.
Furnace: Utilizes the combustion of fuel (natural gas, oil) or electricity to generate heat. The resulting heat is then distributed via a blower fan.
Heat Pump: A reversible system that can either heat or cool a space by extracting and transferring thermal energy between the indoors and outdoors, making it highly energy-efficient.
B. Refrigeration Cycle Components (for Cooling)
Compressor: Known as the "heart" of the system, it pressurizes the gaseous refrigerant, raising its temperature.
Condenser Coil: Usually located outdoors, it allows the high-pressure, hot refrigerant to release its heat to the atmosphere, causing the refrigerant to condense back into a high-pressure liquid.
Evaporator Coil: Located indoors, it allows the liquid refrigerant to absorb heat from the indoor air as it evaporates back into a low-pressure gas, thus cooling the air.
C. Air Distribution Network
Ductwork: A network of channels or pathways used to distribute the conditioned air from the AHU or furnace to the various rooms, and return the air for re-treatment.
Fans and Blowers: Mechanical devices that provide the necessary force to move air through the ducts, overcoming air resistance.
Vents and Registers: Grilles or outlets that regulate and direct the flow of supply air into the space and facilitate the return of air to the system.
D. Ancillary and Control Systems
Filters: Mechanical barriers (e.g., MERV-rated filters) installed to capture airborne particulates, dust, pollen, and other contaminants, enhancing IAQ.
Thermostats and Sensors: The user interface and brain of the system. Thermostats allow for temperature setting, while sensors monitor temperature, humidity, pressure, and air quality to modulate system operation for efficiency and comfort.
III. System Significance
The proper functioning of HVAC systems is crucial for maintaining building integrity and occupant health. Modern HVAC engineering focuses on integrating variable refrigerant flow (VRF) technology and smart controls to not only deliver precise environmental control but also to significantly optimize energy performance in both residential and commercial applications.
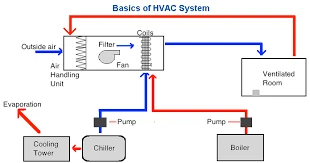

 Process Flow
Process Flow
Sequence
1. Start
2. Controls (Thermostat/Sensors)
3. Air Processing Unit (AHU/Furnace/Heat Pump)
4. Filtration
5. Heating/Cooling Coils
6. Fans/Blowers
7. Ductwork
8. Vents/Registers (Supply Air)
9. Room
10. Vents/Registers (Return Air)
11. Back to AHU
12. End




































