
The Evolution of Generative AI: What to Expect in 2026
In 2025, more than 80% of Fortune 500 companies reported active experimentation with generative AI—yet most admitted they were only using a fraction of its real potential. That gap between adoption and impact sets the stage for what 2026 is poised to become: a turning point year for generative artificial intelligence.
Generative AI is no longer a speculative technology confined to research labs or tech demos. It has become a foundational layer of modern digital infrastructure—powering content creation, software development, scientific discovery, customer engagement, and decision-making at scale. As we approach 2026, the evolution of generative AI is accelerating along multiple dimensions at once: capability, autonomy, efficiency, regulation, and societal impact.
This article explores what to expect from generative AI in 2026, examining technological breakthroughs, industry-specific applications, ethical challenges, and the broader implications for businesses and society. Written from a third-person, authoritative perspective, this analysis provides a forward-looking yet grounded view of the future of AI technology.
1. From Experimental Tools to Core Infrastructure
In its early years, generative AI was largely perceived as an experimental add-on—useful for drafting text, generating images, or assisting with basic automation. By 2026, that perception will be fundamentally outdated.
Generative AI systems are evolving into core digital infrastructure, comparable to cloud computing or databases. Organizations will no longer ask whether to use generative AI, but how deeply to integrate it into workflows.
Key shifts defining this transition include:
Embedded AI: Generative models will be built directly into operating systems, enterprise software, and development platforms.
Always-on assistance: AI copilots will function continuously rather than on-demand, anticipating user needs.
Workflow-native design: Instead of standalone chat interfaces, AI will operate within tools people already use.
By 2026, generative AI will be invisible in the best sense—present everywhere, yet rarely noticed as a separate technology.
2. Multimodal AI Becomes the Default
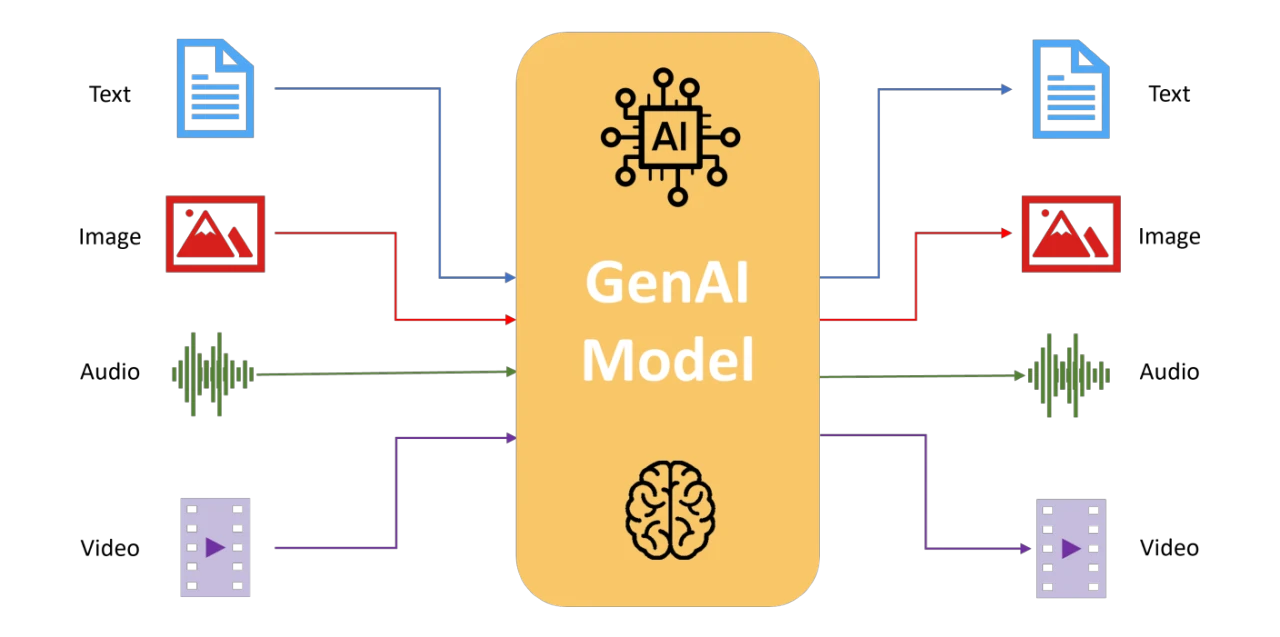
One of the most significant generative AI advancements leading into 2026 is the normalization of multimodal models. These systems can seamlessly process and generate text, images, audio, video, and structured data within a single architecture.
Rather than switching between specialized tools, users will interact with unified AI systems capable of understanding complex, mixed-media inputs.
Practical implications of multimodal AI:
A single prompt can include a document, chart, image, and voice instruction
AI-generated videos will include synchronized visuals, narration, and subtitles
Real-time image and video understanding will support autonomous systems
This shift dramatically expands the scope of generative AI applications, particularly in education, healthcare, design, and engineering.
3. Reasoning, Planning, and Long-Horizon Intelligence
Generative AI in 2026 will move beyond pattern matching toward structured reasoning and planning. While not equivalent to human general intelligence, next-generation models will demonstrate measurable improvements in:
Multi-step logical reasoning
Goal decomposition and task planning
Context retention over long time horizons
These capabilities will enable AI systems to manage complex projects, not just isolated tasks. For example, an AI system may plan a marketing campaign from strategy to execution, adapting dynamically as performance data changes.
The future of generative AI lies not in better answers, but in better thinking processes.
4. Generative AI and Software Development in 2026
Software engineering is one of the fastest-evolving domains for generative AI. By 2026, AI-assisted development will be the industry standard rather than a competitive advantage.
Expected developments include:
AI-first coding environments that generate, refactor, test, and document code
Automated migration between programming languages and frameworks
Continuous security scanning and vulnerability remediation by AI agents
Human developers will increasingly act as architects and reviewers, focusing on system design and oversight while AI handles routine implementation.
This evolution will significantly reduce development cycles and lower barriers to entry for software creation.
5. Industry-Specific Generative AI Applications
By 2026, generative AI growth will be driven less by general-purpose tools and more by domain-specialized models.
Healthcare
Generative AI will support:
Clinical documentation and summarization
Drug discovery and molecular design
Personalized treatment planning
Strict regulatory oversight will shape deployment, but productivity gains will be substantial.
Finance
In financial services, generative AI will enable:
Real-time risk modeling and stress testing
Automated compliance reporting
Personalized financial advice at scale
Manufacturing and Engineering
AI-generated simulations, designs, and predictive maintenance strategies will reduce costs and improve resilience across supply chains.
6. The Rise of Autonomous AI Agents
One of the most transformative AI trends of 2026 will be the rise of autonomous generative AI agents—systems capable of executing tasks independently within defined constraints.
Unlike simple chatbots, these agents can:
Set sub-goals
Interact with external tools and APIs
Monitor outcomes and adjust behavior
Organizations will deploy fleets of AI agents to handle operations such as customer support, data analysis, research, and internal coordination.
Human oversight will remain critical, but day-to-day execution will increasingly be delegated to machines.
7. Data, Synthetic Content, and Model Training
As high-quality human-generated data becomes scarcer, generative AI models in 2026 will rely more heavily on synthetic data.
Synthetic data offers several advantages:
Reduced privacy risks
Controlled distribution of edge cases
Faster iteration and experimentation
However, overreliance on synthetic content introduces risks such as model collapse and reduced diversity. As a result, hybrid training approaches—combining real-world, curated, and synthetic data—will become standard.
8. Efficiency, Cost Reduction, and Edge AI
Another defining trend in generative AI advancements is efficiency. By 2026, the focus will shift from building ever-larger models to deploying smarter, more efficient ones.
Key innovations include:
Model compression and distillation
Specialized hardware accelerators
On-device (edge) generative AI
These advances will reduce inference costs and enable AI deployment in environments with limited connectivity, such as manufacturing floors, vehicles, and medical devices.
9. Regulation, Governance, and Trust
As generative AI becomes more powerful, governance will become unavoidable. By 2026, most developed economies will have implemented formal AI regulatory frameworks.
These frameworks will address:
Transparency and explainability
Data provenance and copyright
Accountability for AI-generated decisions
Organizations that proactively invest in responsible AI practices will gain trust and long-term resilience, while those that ignore governance risks may face legal and reputational consequences.
10. Ethical Challenges and Societal Impact
The evolution of generative AI raises profound ethical questions that will intensify by 2026.
Key concerns include:
Job displacement and workforce transitions
Misinformation and deepfake proliferation
Bias amplification in automated systems
Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between governments, industry leaders, researchers, and civil society.
The impact of AI on society will depend less on what the technology can do—and more on how it is governed.
11. Education and the Future of Learning
Generative AI will fundamentally reshape education by 2026. Personalized AI tutors will adapt content to individual learning styles, pacing, and goals.
Educational institutions will shift focus from rote memorization to:
Critical thinking
Creativity
AI literacy
Rather than replacing educators, AI will augment them—automating administrative tasks and enabling more human-centered teaching.
12. Creativity, Media, and Content Production
In creative industries, generative AI will move from novelty to necessity. By 2026, AI-generated content will be indistinguishable from human-created work in many contexts.
This will transform:
Film and video production
Advertising and marketing
Game design and virtual worlds
The role of human creators will shift toward direction, curation, and storytelling, supported by AI-powered tools.
13. Competitive Landscape and AI Industry Forecast
The generative AI industry in 2026 will be highly competitive, with clear stratification between:
Foundation model providers
Vertical AI solution companies
Open-source ecosystems
Strategic partnerships, proprietary data access, and regulatory compliance will determine long-term winners.
Smaller companies will compete by specializing, while large players will focus on platform dominance.
14. What Comes After 2026?
While 2026 represents a major milestone, it is not an endpoint. The trends shaping generative AI suggest a future where:
AI systems collaborate with humans as peers
Intelligence becomes a commodity
Innovation accelerates across every sector
Understanding the evolution of generative AI today is essential for navigating the technological landscape of tomorrow.
Key Takeaways
Generative AI in 2026 will function as core digital infrastructure
Multimodal, autonomous, and efficient models will define next-gen AI capabilities
Regulation and ethics will shape adoption as much as innovation
Organizations that adapt early will gain lasting competitive advantages
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Will generative AI replace human jobs by 2026?
A: Generative AI will automate many tasks, but it will also create new roles focused on oversight, creativity, and strategic decision-making.
Q: How advanced will AI reasoning be in 2026?
A: AI will demonstrate improved multi-step reasoning and planning, though it will remain domain-specific rather than truly general intelligence.
Q: Is generative AI safe to use at scale?
A: Safety will depend on governance, transparency, and responsible deployment rather than the technology alone.
Conclusion
The evolution of generative AI is entering a decisive phase. By 2026, the technology will be more capable, more autonomous, and more deeply embedded in everyday life than ever before. Yet its ultimate impact will not be determined solely by algorithms or hardware—but by the choices made by organizations, policymakers, and individuals today.
Generative AI is not just shaping the future of technology. It is shaping the future of work, creativity, and human potential itself.






































