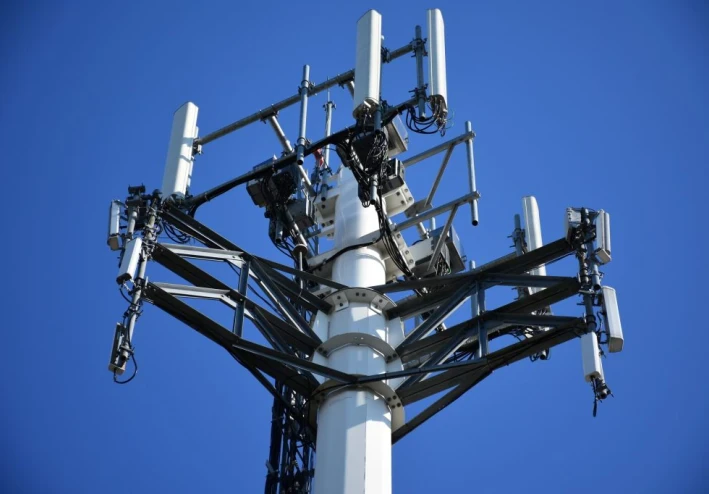

Antennas: Types, Advantages, and Disadvantages
1 reviews
Antennas: Types, Advantages, and Disadvantages

Abstract:
Antennas are fundamental components in wireless communication systems, enabling the transmission and reception of electromagnetic waves. This paper explores various types of antennas, their working principles, advantages, and disadvantages, providing a comprehensive understanding of their applications.
1. Introduction:
Antennas are devices designed to transmit and receive electromagnetic waves, playing a critical role in communication systems such as radio, television, cellular networks, and satellite communications. They come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored for specific applications. This paper discusses the most common types of antennas, their advantages, and disadvantages.
2. Types of Antennas:
2.1 Dipole Antenna:
Description: A dipole antenna consists of two conductive elements, typically straight rods or wires, fed by a balanced transmission line. It is one of the simplest and most widely used antennas.

Advantages:
Simple design and easy to construct.
Omnidirectional radiation pattern (ideal for broad coverage).
Low cost.
Disadvantages:
Limited bandwidth.
Relatively large size for lower frequencies.
Lower gain compared to directional antennas.
2.2 Monopole Antenna:
Description: A monopole antenna is a single conductive element mounted over a ground plane. It is a variant of the dipole antenna.
Advantages:
Compact and lightweight.
Omnidirectional radiation pattern.
Easy to integrate into devices like mobile phones.
Disadvantages:
Requires a ground plane for proper operation.
Limited bandwidth.
Performance depends on the quality of the ground plane.
2.3 Yagi-Uda Antenna:
Description: The Yagi-Uda antenna consists of a driven element, a reflector, and one or more directors. It is highly directional and commonly used for TV reception.
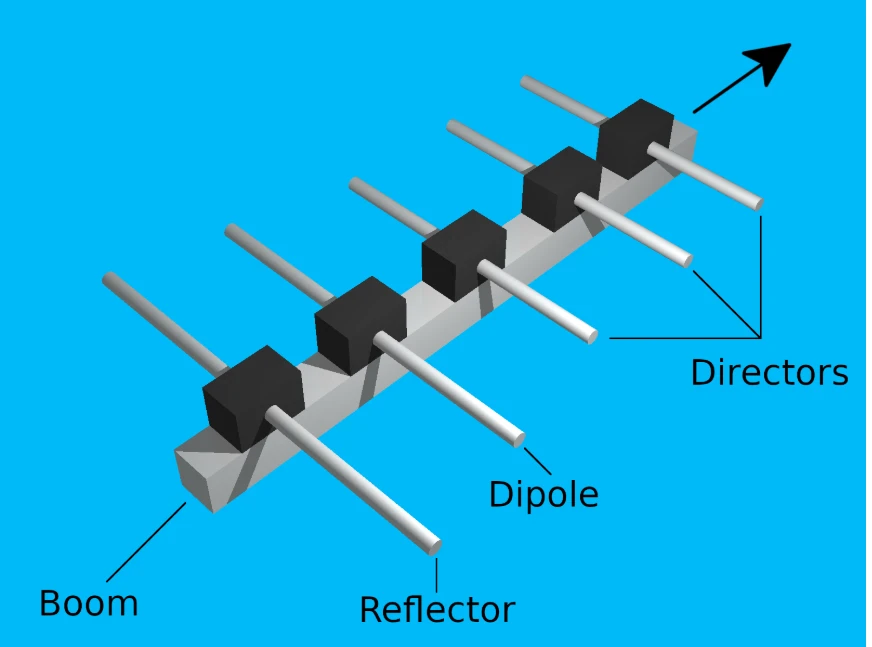
Advantages:
High gain and directivity.
Long-range communication capability.
Relatively simple construction.
Disadvantages:
Narrow bandwidth.
Bulky and requires precise alignment.
Limited to line-of-sight applications.
2.4 Patch Antenna:
Description: A patch antenna is a flat, rectangular antenna printed on a substrate. It is commonly used in wireless devices and GPS systems.
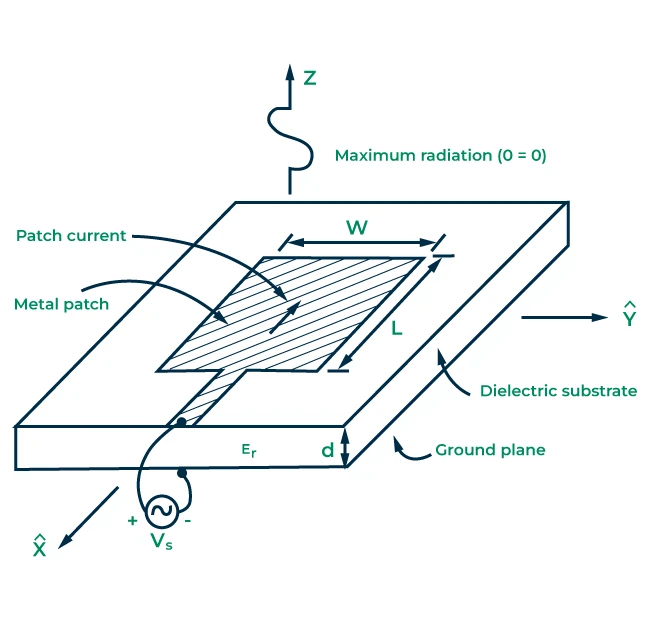
Advantages:
Low profile and lightweight.
Easy to fabricate and integrate into circuits.
Suitable for high-frequency applications.
Disadvantages:
Limited bandwidth.
Lower gain compared to larger antennas.
Sensitive to environmental factors.
2.5 Horn Antenna:
Description: A horn antenna is a flared metal waveguide that produces a directional beam. It is often used in microwave and radar systems.
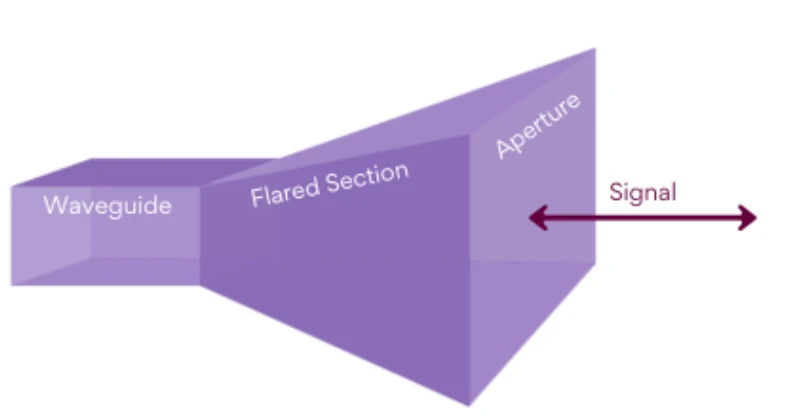
Advantages:
High gain and directivity.
Wide bandwidth.
Low standing wave ratio (SWR).
Disadvantages:
Bulky and heavy.
Expensive to manufacture.
Requires precise alignment.
2.6 Parabolic Reflector Antenna:
Description: This antenna uses a parabolic reflector to focus electromagnetic waves into a narrow beam. It is commonly used in satellite communications and radar systems.
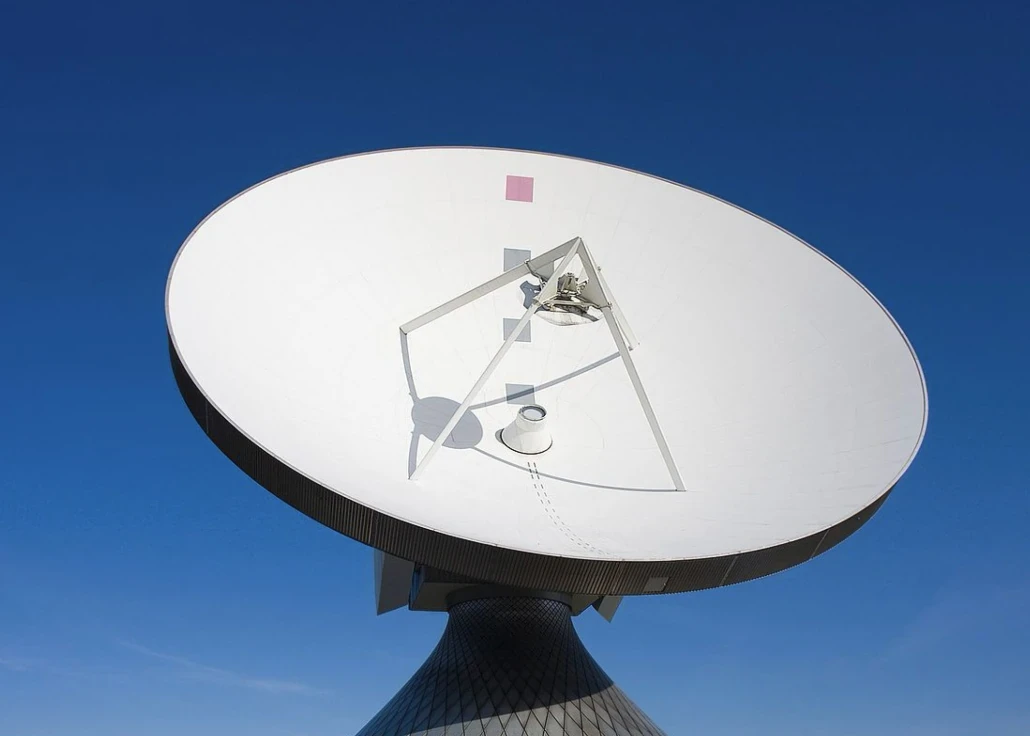

Advantages:
Extremely high gain and directivity.
Suitable for long-distance communication.
Can operate at high frequencies.
Disadvantages:
Large size and heavy weight.
Requires precise alignment.
Expensive to manufacture and install.
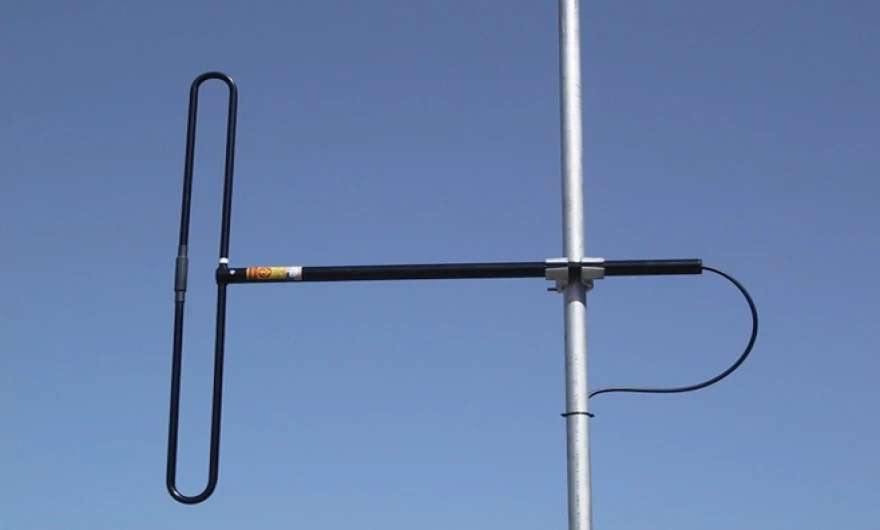
2.7 Loop Antenna:
Description: A loop antenna consists of a loop of wire or other conductor. It can be either small or large, depending on the application.
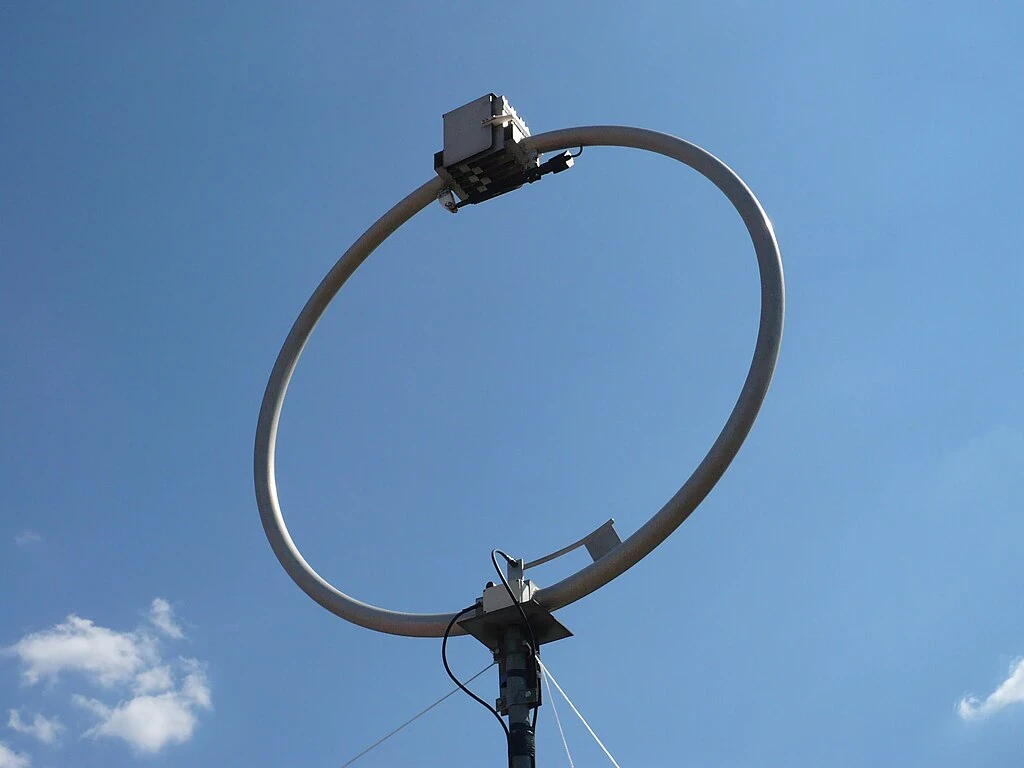

Advantages:
Compact and portable.
Can be omnidirectional or directional.
Suitable for low-frequency applications.
Disadvantages:
Low gain.
Limited bandwidth.
Sensitive to noise and interference.
2.8 Helical Antenna:
Description: A helical antenna is a spiral-shaped conductor, often used for satellite communication and radio astronomy.
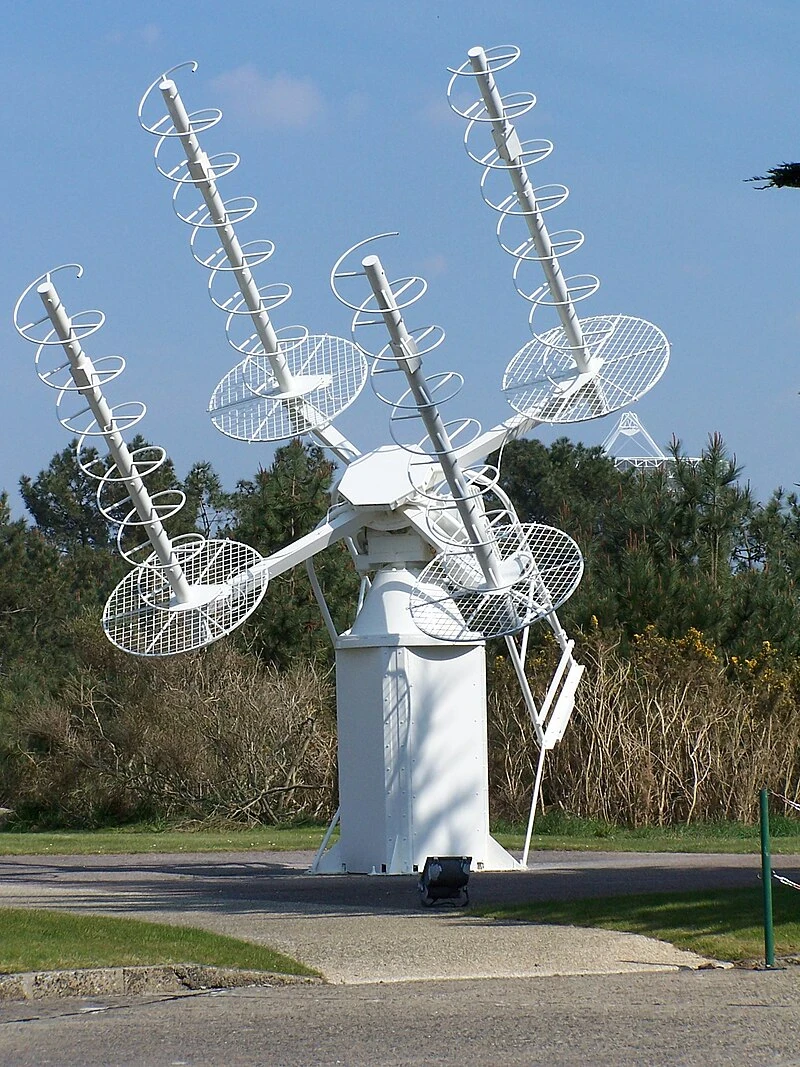
















![article image for اخف واسرع نسخة ويندوز 10 للاجهزة الضعيفة [افضل أداء للألعاب والبرامج]](https://amwcdn.com/featured/137140/conversions/8a5e11ab9b-x-small-featured.webp)













